APA Solution
Introducing an innovative building automation system in the Academy building that saves energy, manages renewable energy and reduces utility costs.
The Research and Innovation Centre Pro-Akademia is an interdisciplinary research unit carrying out research and teaching activities in social and technical sciences. The building in which the company's headquarters is located is a showcase of its values - modern, ergonomic, smart. APA Group had the pleasure to provide Vision BMS software for it, which was installed site by our integrator - Indeos Automation.
Vision BMS allowed to generate savings in utilities consumption, improve control of external and internal roller blinds, manage ventilation and air conditioning, and exploit the benefits of renewable energy in the form of photovoltaic cells, an electric vehicle charging station and a biomass boiler. The system has also been used to measure atmospheric conditions, measuring air, humidity, wind direction and speed, sunshine and CO2 concentration. In addition to the main application, a mobile app and an online app were also developed to remotely manage key building parameters.
Explore technical details
-
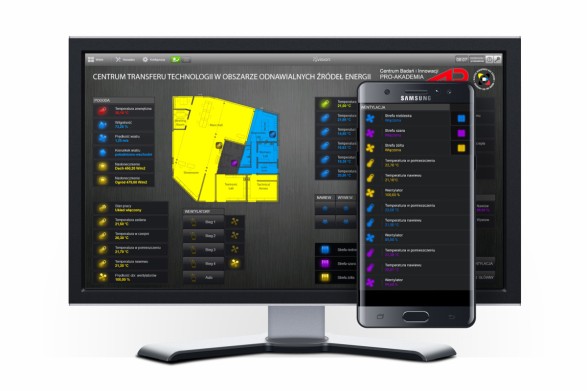
Home screen
The home screen presents basic, general information about the building, such as current weather conditions, temperatures and CO2 concentrations in the rooms, operation status of ventilation systems and energy consumption charts. There are also buttons on the side to switch views
-
External blinds
External blinds have been integrated into the BMS system in a way that makes it possible to control them both from the app and locally using buttons. The blinds were calibrated to determine their position for visualization in the control app
-
Ventilation/air conditioning system
The ventilation system consists of three independent units (air handling unit). Communication is based on Modbus RTU protocol. Remote communication makes it possible to read temperatures at various points in the system (air intake, before/after recuperator, exhaust, supply, etc.), to read temperature presets, and to control fans
-
Photovoltaic system
The 10 kWp photovoltaic system features a Steca inverter. Communication with the inverter was performed using a module from SolarLog, which provides data via Modbus TCP/IP protocol. In addition to the data collected from the inverter, variables comparing weather data (insolation) with electricity production were created, which enabled the calculation of the current efficiency of the photovoltaic system
-
Biomass boiler
Defro's biomass boiler originally had a standalone control system without the ability to communicate with external devices. In order to integrate with the BMS system, two paths were considered: inputting boiler signals to the Wago controller, or creating our own control algorithm based on information provided by the manufacturer, or replacing the boiler controller with a newer one that allows communication via theInternet. Unfortunately, also the newer controller did not allow integration with Vision BMS. As a compromise solution, the boiler control application was displayed in a web browser on the same computer where Vision BMS is installed
-
Electric vehicle charging station
Garo Efacec electric vehicle charging station has its own communication protocol suitable for communicating with other charging stations over the Internet. It also features a web-based user panel. Nevertheless, the exchange of data regarding the current charging and historical transactions available on the above-mentioned website was originally only possible by means of a data file export. Direct discussions with the supplier ruled out the possibility of implementing an industrial protocol (e.g. Modbus) for a single installation. However in order to be able to display and archive charging transaction data in the BMS system, an auxiliary application has been created which reads data from the user panel (parsing data from the page), which is then made available using a virtual Modbus TCP server. In this way the Vision BMS application can display the current charging data and the cumulative values of historical transactions (e.g. the amount of transferred energy for charging)
-
Heat and electricity meters
Heat and electricity meters communicate with the Wago controller via M-Bus protocol. The data is refreshed every few tens of seconds. A time differential is calculated from the readings of all the meters to display both the total energy transmitted by a given meter over a specific time period and the current averaged electrical or thermal output. Meter readings are displayed in the application as daily, weekly or annual data, thus enabling the observation of long-term trends
-
Weather measuring devices
Measurement of atmospheric conditions consists of measurements of air temperature, humidity, wind direction and speed, and insolation. The data generated by the measurement devices are collected in the LBX device and sent to the Wago controller, where - through a Modbus TCP protocol - they are sent to the Vision BMS system. The same goes for indoor temperatures and CO2 concentration measurements. Wind speed measurements are plotted as average and maximum values to record gusts